Testing
Testing
In the General tab, you can view the domain name for the distribution. When you access this domain, your request is routed to the nearest edge location. And if the content is not in the edge cache or regional cache, it is forwarded to origin which is this case is our S3 bucket.
- Copy url + test.html
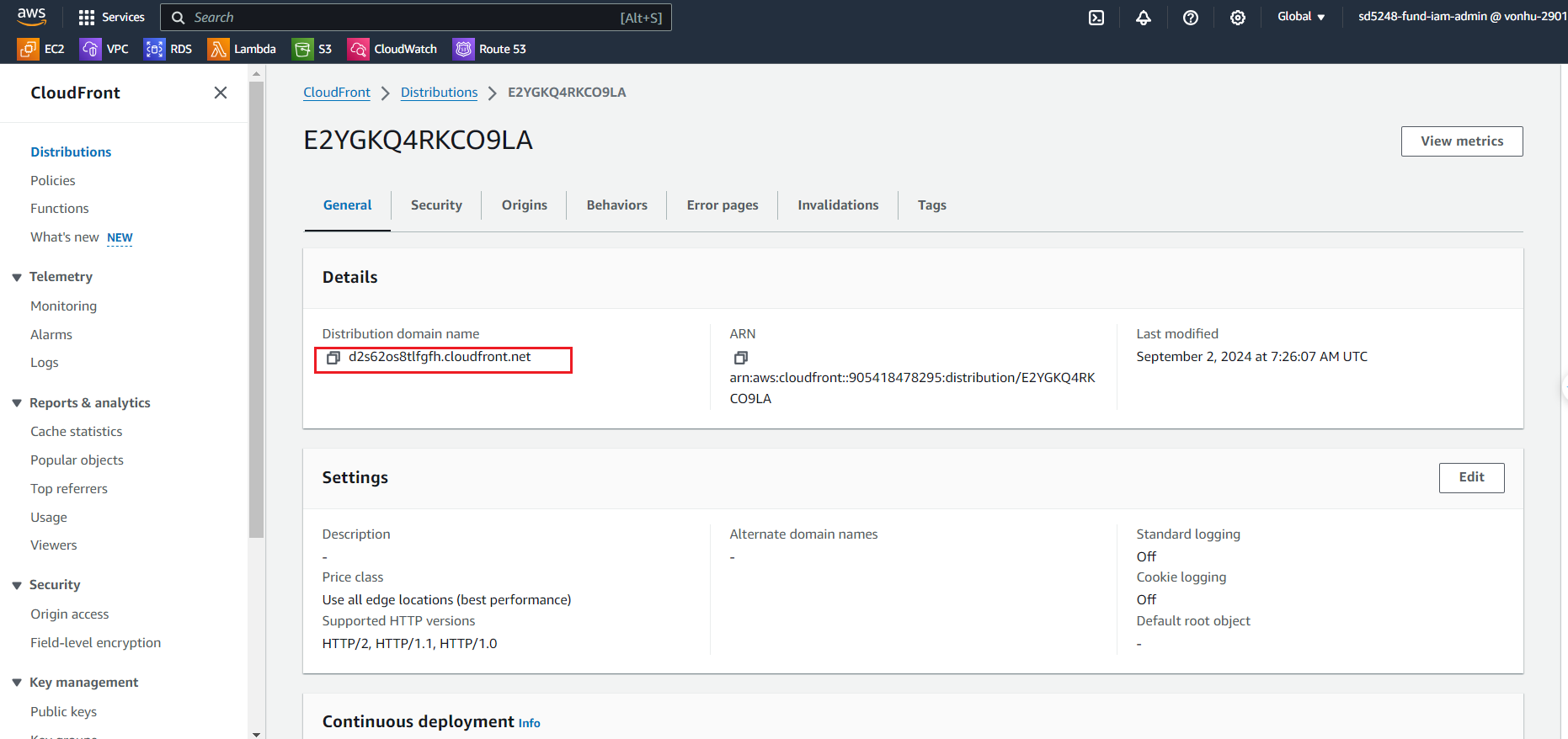
- Try open link:
https://d2s62os8tlfgfh.cloudfront.net/test.html
The response is cached at the edge location for serving other requests.

Update HTML
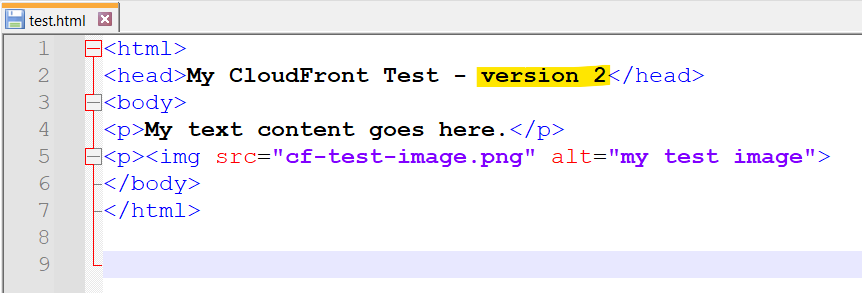
- Now let’s update the HTML page in the S3 bucket. We are going to update the test html version to 2. Save the file locally and then upload to your S3 bucket.
- Update the HTML object to S3 bucket (version 3 -> version 2)
- Now if you open the page using S3 bucket URL in a different browser tab, it renders the second version of the page. This is because the content is getting directly from S3
- Reupload test.html to ws1-cloudfront bucket
- Open test.html by S3 Object URL:
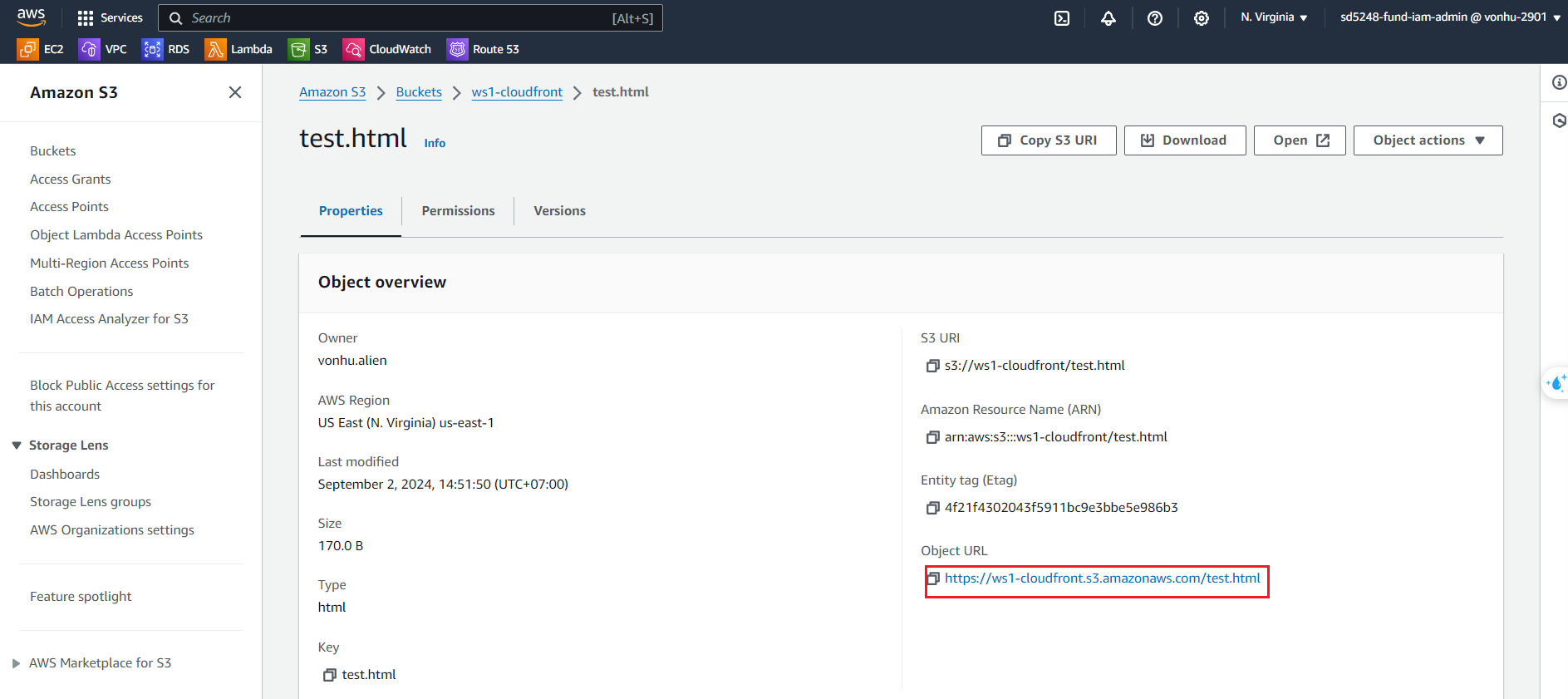

- On the other hand, if you refresh the CloudFront page in the browser we opened it before, it renders the cached content, which is version 3. The content is reused from cache expires for this page and image.
By default, CloudFront caches S3 objects for 24 hours
- Open test.html by CloudFront
it renders the cached content (content was not updated)

Notes:
In this lab, we set up an S3 bucket as an origin and we configured a CloudFront distribution.
There are two issues that we identified with this setup.
- The S3 bucket is public.
- Content is cached for 24 hours.
Look at controlling the cache duration in next lab!